HSE Management System
Oil India Limited is fully committed to Safety, Health & Environment and the same is reflected in the HSE functions and systems that have become part and parcel of the total management and work culture of OIL. These systems provide structured paths for improvement of communication, accomplishment of goals, development of personnel and overall improvement of business process. Safety, Health & Environment is an integral part of our business performance. An integrated approach has been established for interlinking all types of disciplines/ activities with HSE matters to demonstrate proactive Safety culture.
HSE Management is an integral part of overall management system at OIL right from inception, realizing that higher productivity can only be achieved through safe procedures and practices. Hence, HSE Management became the focal point of all developmental activities. To provide direction for various safety related activities and to ensure adequacy of funds for effective implementation of these activities, OIL has a separate department with dedicated and well qualified personnel with well-defined HSE Policy wherein the Company is committed to safety of its employees and the people, machines and environment associated with it including those living in the neighbourhood.
HSE Policy in OIL lays stress on safe facilities and work environment, safe work procedures and effective training for prevention of accidents and consequent downtime and maintain highest standards of occupational health, safety and environmental protection.
To meet the above objective, OIL has established policies, systems, procedures and guidelines to achieve world class HSE standard as detailed below:-

Safety manuals, Rules and Regulations
The OIL Safety Management System is to provide the framework and structure for the delivery of the highest level of HSE Performance in accordance with the best exploration, production and transportation practice. The SMS will be continually evolved to respond to changing needs and emerging operational requirements as the organization is going through a period of transition. Amongst the various documents in the HSSE management system, the manual is the most important and essential document. The specific purpose of the Manual is to document the core elements of the HSSE management system, their relationship and interaction.
The QHSSE Guidance Manual lays down the generic principles for implementing a holistic management system. It encompasses a ‘best practice approach’ towards occupational health risks, occupational safety risks, process safety risks, environmental risks, quality risks, business processes risks and task risks, and management activities including leadership, planning, human resources, statutory compliance, project management, training and competence, communication and promoting QHSSE, asset management, contractor management and purchasing, emergency preparedness, learning from events (positive practices as well as undesirable incidents) and management review of results.

Statutory & Regulatory Authorities
- Directorate General Of Mines Safety (DGMS)
- Oil Industry Safety Directorate (OISD)
- Petroleum and Natural Gas Regulatory Board (PNGRB)
- Petroleum & Explosives Safety Organization (PESO)
- Ministry of Environment, Forest & Climate Change ( MoEF & CC)
- Central & State Pollution Control Board (CPCB & SPCB)
- Commissioner of Labor

Audits, Inspections and Compliance Monitoring
HSE department carries out and coordinate regular safety audits and inspections covering all the installations. To add value and increase effectiveness to our Pre-spud and Pre-workover Safety Audits, the system of inspection has been reworked and checklists are being updated time to time so that it will cover not only OIL’s HSE Policy commitment but also statutory requirement like OMR, OISD, PESO, PNGRB, IBR, etc. A system of Multidisciplinary audits is available where audits are conducted by teams consisting of members from Safety department and other operation related departments at various Production and Engineering installations (Internal Audits). Review audits of audit recommendations were conducted at Drilling, Production and Engineering installations. A system of monitoring installation wise compliance of audit recommendations is put in place. Also, regular Surprise Safety Inspections are carried out in our operational areas to check the efficacy of the HSE management system. In addition to the above, External Safety Audits by DGMS, OISD etc. are conducted from these agencies as per the schedule and compliance of recommendations are updated and submitted as per the timeline fixed by the authorities.

Hazard Identification
A systematic approach is used to identify all foreseeable hazards, effects, threats and consequences associated with the activities, products and services. Methods will depend on the level of complexity and previous risks associated with the operation. They include:
- Experience based judgment.
- Structured review techniques
- Use of pre-prepared Checklists.
- Use of Industry accepted Codes, Standards, and Guidelines
Risk Assessment
Risk is a component of consequence and severity.
It is measured as:-
Risk = Severity of hazard X likelihood of occurrence.
The risks associated with the previously known hazards are identified. A risk is assessed by determining the hazard consequences (magnitude and severity) together with consequence likelihood. As part of predicting the consequences of hazards, the risk assessment is characterization of the populations (including third parties), assets and environments that could be impacted, including identification of sensitive receptors and targets (locations, numbers involved and proximity).

Standard Operating Procedures
Standard Operating Procedures are stepwise written guidelines for procedures and tasks involving recognized hazards. SOP plays a vital role in guiding our personnel to follow proper safety procedure, prior to commencement of any job. Following SOP meticulously, one will surely be able to minimize the risks and hazards in the workplace to As Low As Reasonably Practicable. Besides, the work procedures documented on the SOP also covers all the requirements of statutory guidelines as per OMR, OISD Standards etc.

Permit to Work
The objective of the Permit to work procedure is to identify hazards associated with a nonroutine job, and to develop precautions required to control against each identified hazard. The work in hydrocarbon processing/ handling industry is associated with unusual risks, therefore, to provide safe working conditions and to carry out the work safely, a standardized & uniform procedure will act as a guide.

Safety Critical Equipment Bypass and Restoration Management
The primary objective of the “Safety Critical Equipment Bypass and Restoration Policy” is to evaluate and mitigate risk for all occurrences where safety critical equipment is bypassed, and to ensure the bypass is performed in a safe and controlled manner. Moreover, whenever there is need to bypass the Safety Critical Equipment whether it is routine or emergency, the appropriate approving mechanism should in place so that the information should be known to the respective officials to respond with desired preparedness in case of any eventuality.

Management of Change
Changes in the organization, management, personnel, equipment, processes and procedures of an activity have the potential to create adverse consequences to HSSE performance and/or affect the existing risk assessment results. The Management of Change process is therefore critical for ensuring that any changes to the original concept, design, equipment, assumptions, codes, standards, processes, or HSSE Management System aspects (E.g.:- legislation, organizational structure, responsibilities) are recorded and fully assessed for their impact prior to the change being implemented.

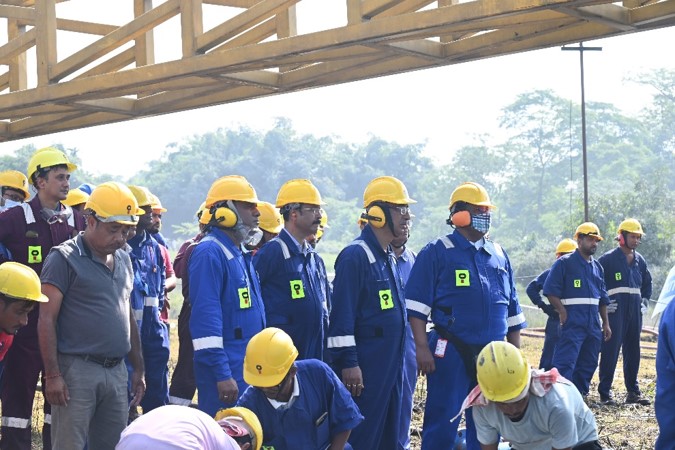
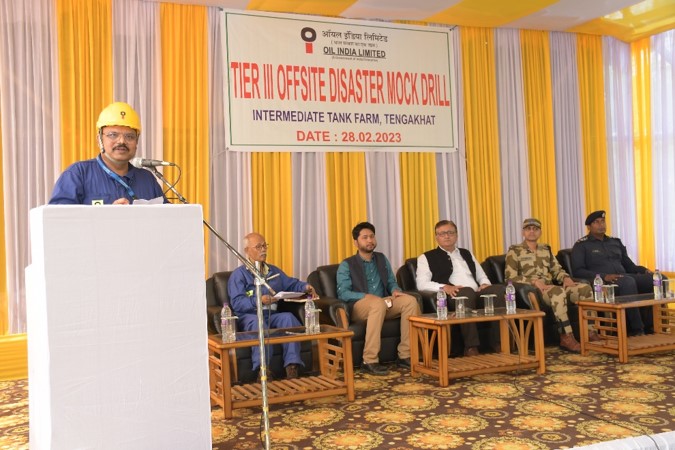
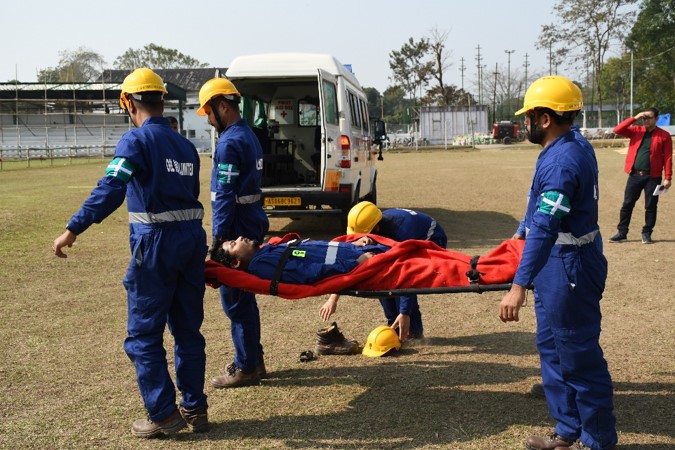
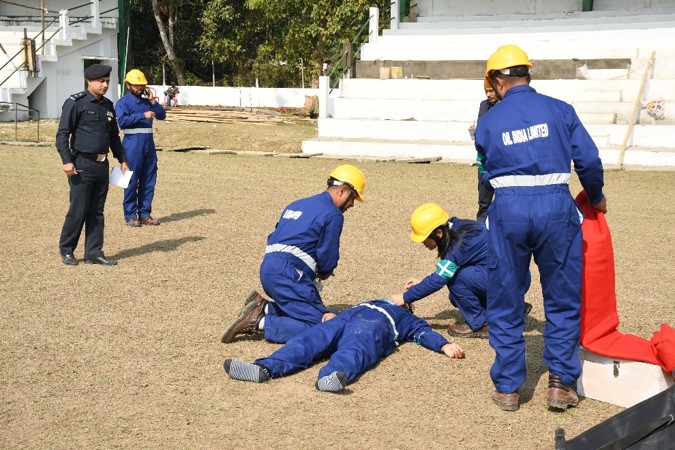
Emergency Preparedness & Mock Drills
OIL has a structured system in place to enable effective and efficient response to serious incidents. The effective plans are in place throughout the company to manage serious incidents at the appropriate level and to affect the speedy resolution of critical business processes and services. A fourtier disaster management plan is maintained in OIL to ensure that appropriate actions are taken, management and resources are deployed in response to significant incidents anywhere within our operations.
Contractor Personnel Safety Management
It is OIL’s policy to ensure that contractors also operate a management system that is consistent with the requirements of this HSSE Management System. Interfaces between this system and contractors’ and subcontractors’ systems will be considered so that any differences and conflicts may be resolved. The scope of work in the contract document shall clearly indicate the HSSE requirements of OIL. Moreover a well defined Bridging Document with RACI Charts are developed before initiating the work.

Accident Reporting, Investigation and Analysis
Incident reporting and recording is an important tool for a healthy safety management system. The other aspect is the learning from incidents. The post investigation root cause analysis and remedial measures leads to reductions in incidents, indicates requirement of additional controls for reducing hazard and risks, improves Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs), and many more. The prime objective of accident investigation is Accident prevention. Accident prevention includes all measures taken in an effort to save lives, escape from injury, reduce the degree of injury, avoid damage to property and prevent the loss of productive time.

Personal Protective Equipment
When there is a hazard to personal safety or health at work, it is most important to eliminate the hazard by adopting safety measures like engineering controls, improved work processes and administrative controls. PPE should be used only when these measures cannot control the hazards effectively. The main purpose of PPE is to protect the body of the user from contact with the hazards, but not to eliminate the hazards. Since the effectiveness of PPE can be easily affected (e.g. by improper wearing), PPE should only be regarded as the last resort in the hierarchy of hazard control measures. It is a supplement to other measures, but not a substitute for them.
HSE Trainings
OIL will emphasize on creating awareness among the staff and the contractor employees about safety awareness. This will be achieved through safety communications (group and one to one) using daily safety/tool box meetings, on site trainings, posters, notice boards and targeted campaigns as medium. OIL will also provide appropriate safety leadership and HSSE awareness training to all concerned.

Stop Work Authority
It is a tool to empower personnel at workplace with the responsibility and obligation to stop work when a perceived unsafe condition or behavior may result in an undesired event, or if they see that any of their co-worker may be in immediate danger in the workplace. The stopped work can be resumed again only after all the issues and concerns have been adequately addressed and after implementation of corrective measures as per the risk assessment.
Occupational Health Monitoring
The successful implementation of Management Plans and Policies greatly depend on the adaptability by the employees, who are the prime movers of the progress of company. Maintaining their health is very much vital for productivity & effectiveness. To promote the health of our employees, OIL has made a structured Occupational Health Monitoring system so as to have scientific basis for decisions aimed at protection of employee’s health from any possible adverse consequences of exposure to occupational health hazards. Following systems are followed in OIL towards providing Occupational Health Services:
- An Occupational Health Service (OHS) Centre is established at Duliajan. Various activities co-ordinated are pre-employment, periodical and pre-retirement medical examination
- Conducting First Aid Training & other awareness programme related to Occupational Health Hazards & remedial measures.
- OHS in peripheral areas are provided through dispensaries located in our Oil fields at Moran, Jorhat and Sonapur etc.
Employees Participation
OIL has taken utmost care to involve the employees in Safety circle & Safety culture through their obligations and commitment towards achieving HSE performance.
- Different Safety motivation programme/competitions are conducted.
- Employee’s participation in Pit level safety committee meeting & Departmental Safety Committee meeting, Management Safety committee meeting & Tripartite meeting
- Suggestion schemes
- Regular interaction through meetings with Recognized Workers Union.

Colour Code Policy
Schemes for identification of the contents of piping systems have been developed in the past by a large number of industrial plants and organizations of various kinds. The policy arrived at individual cases may have met the requirement of respective agency but might have suffered from a lack of uniformity. Numerous injuries to personnel and damage to property have occurred because of mistakes made in turning valves on, or disconnecting pipes at the wrong time or place, particularly when outside agencies, such as mutual aid partners, were called into assist. In order to promote greater safety and minimize the chances of error, confusion or inaction, especially in times of emergency, a uniform system for the identification of piping contents has been established to warn personnel when the piping contents are inherently hazardous.

Aspect Impact Monitoring
OIL is dedicated to the monitoring and upkeepment of the surrounding environment in all its operational areas. This is obtained by following the Aspect Impact Guidelines of OIL. The objective of this is to provide guidance for evaluating the various aspects of OIL’s activities and its impact on the operational areas. The evaluation should result in a determination of whether or not a particular aspect has any significant environmental impacts and if so, whether or not the concerned department/installation can control or influence those impacts. Those activities that are identified through this procedure as having significant and controllable impacts will then be reconsidered in the procedure to determine objectives and targets for controlling the identified impacts
Safety Campaign and other activities
Bringing awareness on safety is one of the most important functions of the Department. As a part of Safety Campaign, various kinds of activities foe safety awareness are being organized every year. During the safety campaign, apart from the internal inspections of the various installation and subsequent evaluation for awards, various competitions like poster, slogan, First-Aid, Drama, Skit, etc. are organized for the employees, contractor personnel and their families.

Record Keeping & Documentation
The record keeping is an important aspect of HSE Management System. The records helps us in visualizing the actual status of man, machine and materials. This is also considered as a reference guide to the people reminding the history of the past incidents and lessons learnt in those incidents. Record keeping is the best mean to communicate information and avoid waste of time in duplication of effort. The written report prompts people to remember what they have to and how to do it. This shows people’s commitment and concern for HSE aspects of the installation
Performance monitoring and system evaluation
HSE performance measures and indicators are identified and documented. Active monitoring programmes are established and maintained based on the HSE performance measures and indicators, with the depth and frequency of inspections, examinations and measurement reflecting the nature and extent of the risks involved. The main objective is to ensure that HSE plans are being implemented and that objectives and targets are being met and that risk controls have been implemented and are effective. This helps to learn from HSE management system successes and failures and provide information to review and improve HSE management and performance. This ensures that legislative compliance is monitored.
- Ambient Air quality monitoring installations
- Stack Monitoring of DG sets.
- Noise Level Monitoring at installations
- Noise reduction through acoustic enclosures and sound barriers
- Internal Environmental audit
- Use of water based mud.
- Disposal of E waste in safe and scientific manner through authorized recyclers
- Disposal of batteries through authorized recyclers
- Disposal of Hazardous waste
- Drilling installations are equipped with ETPs
- Flare pits are enclosed to minimize the heat and light around the area
- Oil Spill Contingency Plan is in place.
- Well abandoned policy include restoration of sites as per statutory guidelines
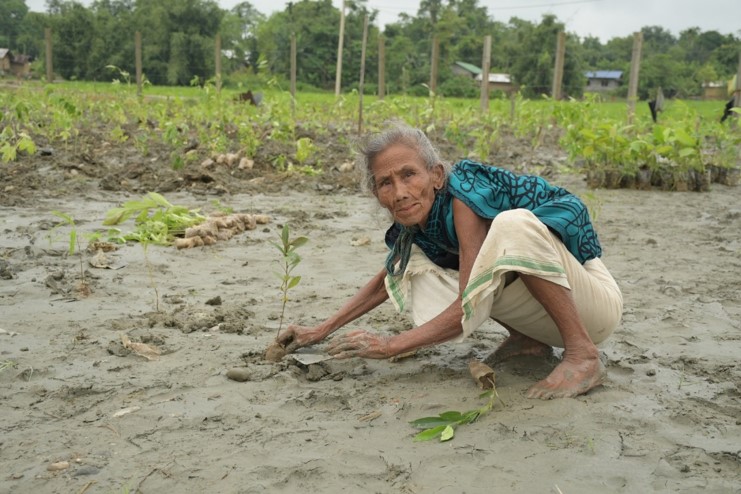
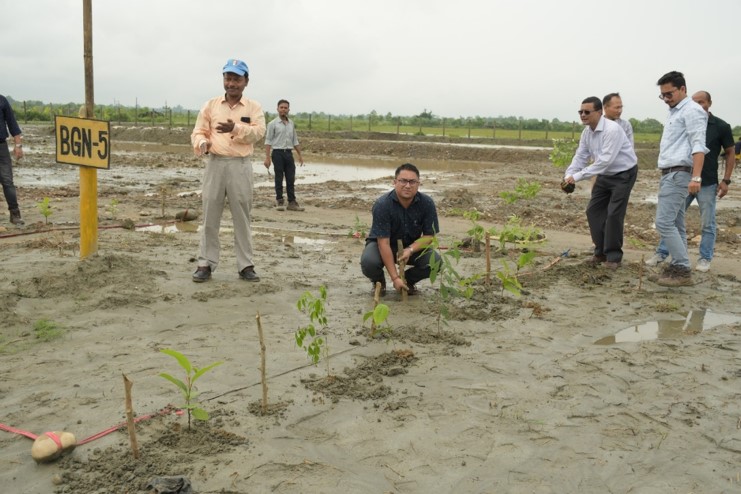
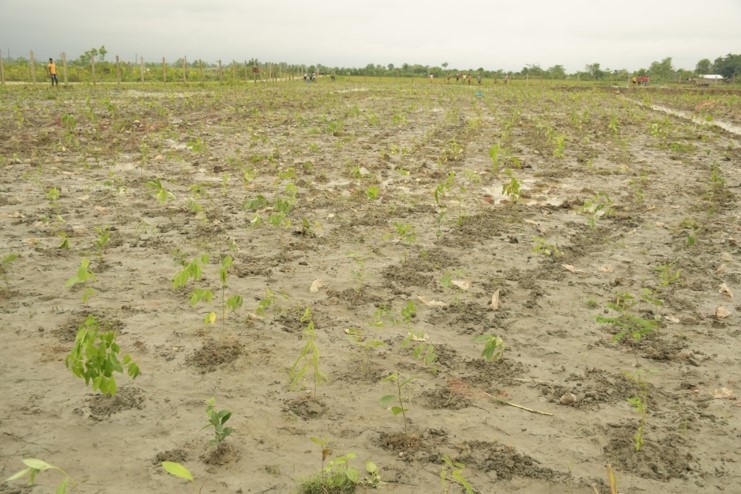
- Mass tree plantation at abandoned well sites to GHG emission and offset Carbon Footprint.
- Bioremediation of oily sludge through in-house developed bacteria.
- Subsidence and Biodiversity Study as per recommendation of statutory authorities.
- Promoting clean energy through gas, solar and wind energy.
- Promoting Rain Water Harvesting in various installations
- Observance of World Environment Day.
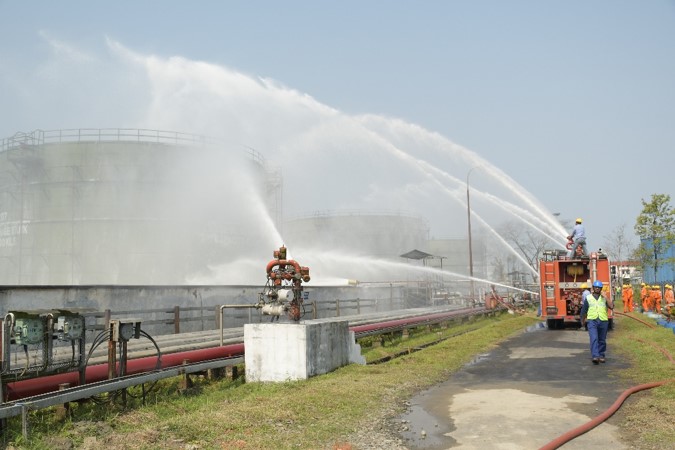
The fire protection arrangement in oil and gas industry is based on Fire Safety, Loss Prevention and Control. It considered that in the hydrocarbon industry, the risk of fire is omni-present at all levels of operational activities like exploration, drilling, production, processing & transportation, Critical operations requirement, and large inventories stored at facilities. A fire in one part of these operational areas can endanger to other parts of the area, if not controlled or extinguished as quickly as possible to minimize the loss of life & property and prevent further spread of fire.
The fire protection arrangements at Oil India Limited (OIL) involve comprehensive measures to ensure the safety of their operational areas, establishments, and society at large. Here are some key aspects of fire prevention & fire protection system(s) as given below:
Fire Stations: OIL operates two full-fledged Fire Stations at Duliajan and Moran, covering the upper Assam Oil & Gas field areas. Additionally, there is a Satellite Fire Station at Kumchai in Arunachal Pradesh to address fire prevention, protection, and firefighting in the oil field areas of Arunachal Pradesh which are being managed by company resources.
Further, to improve the response time during any fire emergency in the far flung or remote OIL’s operational areas, Satellite Fire Stations (02Nos) have been commissioned at Makum & Tengakhat through Service Contract.
Track Record: The OIL Fire Service has a commendable track record in mitigating well fires, other major industrial fire emergencies as well as public fires in OIL’s operational areas of Assam & Arunachal Pradesh.
The Fire Service operates round the clock and is fully equipped with State-of-the-Art robust fire fighting equipment & Appliances to handle all types of fire emergencies.
Accreditations: Fire Stations at Duliajan and Moran are accredited with ISO certifications for Quality Management System (ISO-9001:2015), Environmental Management System (ISO-14001:2015), and Occupational Health and Safety Management System (ISO-45001:2018).
Collaborative Arrangements: Mutual Aid Agreements are also in place with nearby industries and State Fire Services to provide support during any major fires or blowouts. This collaborative approach ensures that even in remote areas, there is support available for handling fire emergencies
Firefighting Systems/Equipment: Installations are equipped with necessary fixed and portable firefighting equipment, complying with national and international statutory codes and standards such as OISD, OMR-2017, PNGRB, BIS, NFPA, UL Listed, etc. These equipment/ systems are mainly –
- First-Aid (Portable) Fire Fighting Equipment
- Fixed Fire Fighting System
- Mobile Fire Fighting Appliances
The provision of necessary portable & fixed fire fighting equipment/system are taken care right from the design stage of an installation and time to time its adequacy is being reviewed by the expert committee due to the change(s) in statutory standards.
Fire Safety Audits: The fire safety audit is a systematic, critical examination of all potential fire hazards in the installations/ establishments and relevant documents to ascertain how the installations are being managed regarding fire safety. The fire safety audits are being carried out in our installations on regular basis as per various statutory standards, codes & practices.
Training Programs: A systematic training programs are being conducted throughout the year to enhance fire safety awareness and develop fire fighting skills amongst employees of all installation’s personnel.
To further enhance the fire fighting capability of installation’s personnel across the company as well as outside industries, simulated Live Fire Fighting Trainings are also being imparted at Central Fire Station, Duliajan.
Moreover, Advanced Fire Fighting Training (Duration: 04Days) for all field going employees and executives of OIL are also being imparted to comply the statutory guidelines as per OISD-STD-176 which mainly covers all crucial fire fighting concepts & strategies along with hands-on training on all critical fire fighting equipment which are deployed in OIL’s installations.
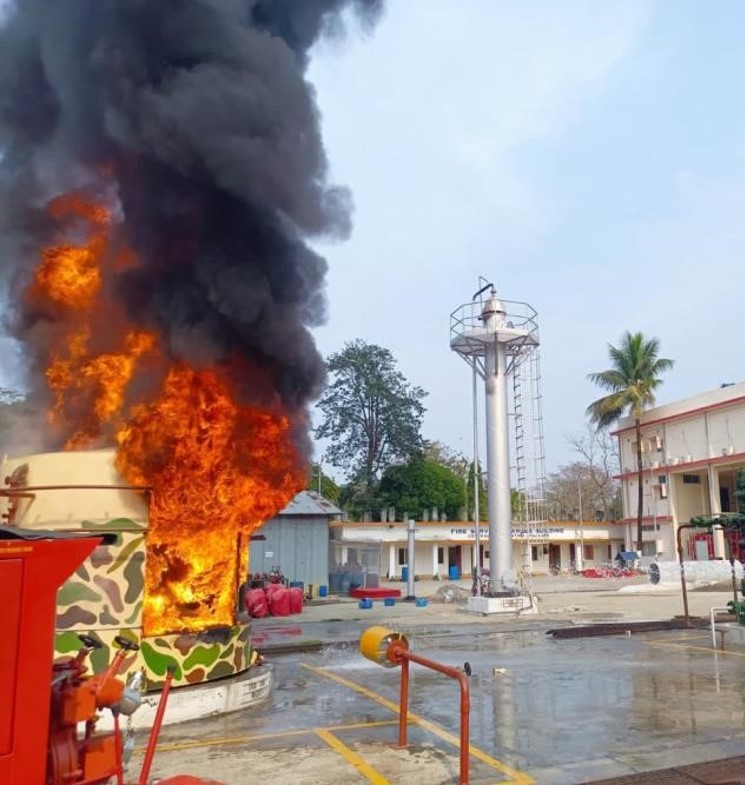
Live Fire Training Ground: To cater the requirement of practical fire fighting training in most efficient manner, OIL Fire Service has developed a training ground containing various simulated live fire fighting modules. These modules are supplied with pressurised oil and gas and exposed to source of ignition to put these modules on fire.
Water ring main and various fixed fire fighting systems (Hydrant, water/ foam monitors, water spray system, foam pouring system etc.) are installed in the training ground which will be pressed into operation to fight the live fire on the various modules. This type of live fire fighting training will boost the courage and confidence level of field personnel to handle actual fire situation at their workplaces with the fixed firefighting systems available in their respective installations. To meet the requirement of different kinds of installations of Oil India Limited, the various types of modules are installed. These modules are:
| Sr. No. | Title |
|---|---|
| 1. | X-Mass Tree Fire |
| 2. | Tank Fire, |
| 3. | Column Fire |
| 4. | Vertical Flange Fire |
| 5. | Horizontal Flange Fire |
| 6. | Pit / Broaching Fire |
| 7. | Smoke House |
| 8. | Tunnel |